In the dynamic and often perilous world we inhabit, personal safety is paramount. Whether in professional environments such as law enforcement, security services, or in everyday life scenarios, the need for protective gear is ever-present. Among the various types of protective materials, cut-resistant fabrics stand out for their ability to safeguard individuals from sharp objects and potential harm. This article delves into the fascinating world of cut-resistant materials, exploring their composition, applications, and the science behind their effectiveness.
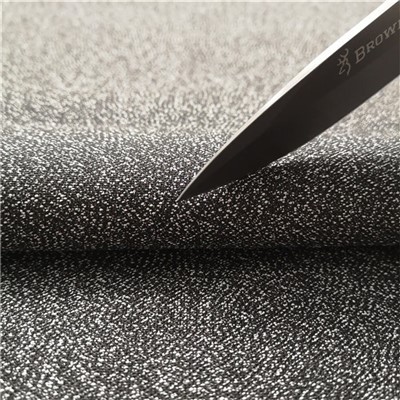

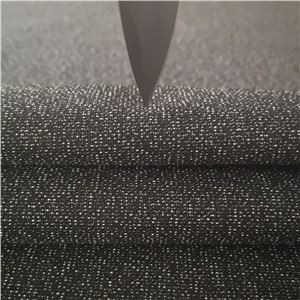
Cut-resistant materials are specifically engineered to withstand damage from sharp objects such as knives, blades, and other cutting tools. These fabrics are designed to provide a barrier that resists penetration and minimizes the risk of injury. The effectiveness of a cut-resistant material is determined by several factors including the type of fibers used, the fabric structure, and the manufacturing process.
There are several types of cut-resistant materials, each offering unique properties and levels of protection:
Aramid Fibers (e.g., Kevlar): Aramid fibers are synthetic fibers known for their high strength and heat resistance. Kevlar, a well-known aramid fiber, is five times stronger than steel on an equal weight basis. It is widely used in bulletproof vests, helmets, and cut-resistant gloves.
High-Performance Polyethylene (HPPE): HPPE fibers, such as Dyneema and Spectra, are known for their exceptional strength and cut resistance. These fibers are lightweight and provide excellent protection, making them ideal for use in gloves, sleeves, and other protective clothing.
Stainless Steel Fibers: Stainless steel fibers are often woven into fabrics to enhance cut resistance. The metal fibers provide a high level of protection against sharp objects, making them suitable for use in industrial settings where workers handle sharp tools and machinery.
Fiberglass: Fiberglass is another material used in cut-resistant fabrics. It offers good cut resistance and is often combined with other fibers to enhance the overall protective properties of the fabric.
Sainfabric: A newer addition to the cut-resistant fabric family, Sainfabric is both lightweight and breathable while providing exceptional resistance to stabbing and cutting. This material stands out due to its ability to offer high-level protection without compromising on comfort or appearance, making it ideal for discreet protective clothing.
The effectiveness of cut-resistant materials lies in their structure and the properties of the fibers used. When a sharp object comes into contact with a cut-resistant fabric, several mechanisms come into play:
Fiber Strength: The inherent strength of the fibers resists penetration by the sharp object. Stronger fibers like aramid and HPPE can withstand higher levels of force without breaking.
Fabric Weave: The way fibers are woven together plays a crucial role in cut resistance. Tight weaves and complex structures can trap and blunt sharp objects, reducing their ability to cut through the material.
Layering: Many cut-resistant fabrics are made up of multiple layers of different materials. This layered approach creates a more effective barrier against sharp objects, as each layer contributes to the overall strength and cut resistance of the fabric.
Cut-resistant materials have a wide range of applications across various industries:
Law Enforcement and Military: Police officers and military personnel often wear cut-resistant clothing and gloves to protect themselves from knives and other sharp objects during confrontations.
Industrial Safety: Workers in industries such as manufacturing, construction, and glass handling are at high risk of cuts and lacerations. Cut-resistant gloves, sleeves, and aprons help protect workers from injuries caused by sharp tools and materials.
Sports and Recreation: Certain sports, such as fencing and ice hockey, involve the use of sharp equipment. Cut-resistant materials are used in protective gear to safeguard athletes from potential injuries.
Healthcare: Medical professionals, especially those working in emergency and surgical settings, can benefit from cut-resistant gloves and clothing to prevent injuries from sharp instruments.
Everyday Use: Cut-resistant clothing is becoming increasingly popular for personal use. Individuals seeking extra protection in their daily lives can wear discreet cut-resistant shirts, jackets, and accessories made from advanced materials like Sainfabric.
When selecting cut-resistant materials for specific applications, it is essential to consider the level of protection required, the comfort and breathability of the fabric, and the overall durability. For instance, while Kevlar and HPPE offer high levels of cut resistance, they may not be as comfortable or breathable as newer materials like Sainfabric. Therefore, the choice of material should balance protection with wearability to ensure users are both safe and comfortable.